Pursuing a graduate degree at a top U.S. university is a significant academic achievement and a substantial financial investment. However, the cost of tuition, fees, and living expenses can be daunting. Fortunately, many top universities offer a range of scholarships, fellowships, and financial aid options to help students manage these costs. This article explores the various types of scholarships and financial aid available to graduate students at leading U.S. universities, providing insights on how to secure funding for advanced studies.
Types of Financial Aid Available
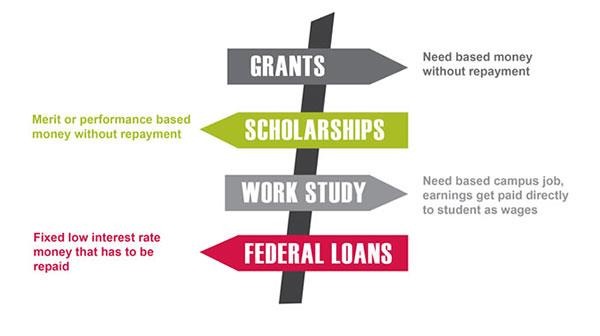
Graduate students at top U.S. universities can access a variety of financial aid options, including:
- Merit-Based Scholarships
- These scholarships are awarded based on academic achievements, leadership qualities, and other outstanding characteristics. Merit-based scholarships often cover tuition, fees, and sometimes living expenses.
- Example: The Harvard Graduate School of Arts and Sciences offers several merit-based fellowships, such as the Merit Fellowship, which provides full tuition coverage and a stipend for living expenses.
- Need-Based Financial Aid
- Need-based aid is awarded based on the financial situation of the student or their family. This type of aid often includes grants, work-study opportunities, and subsidized loans.
- Example: Yale University offers need-based aid through its Graduate Financial Aid Program, which includes grants and low-interest loans to cover the cost of attendance.
- Research Assistantships (RAs)
- RAs are positions that involve working on research projects under the supervision of faculty members. In exchange, students typically receive a stipend and tuition remission.
- Example: The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) offers research assistantships that cover full tuition and provide a stipend for living expenses, often in areas such as engineering, science, and technology.
- Teaching Assistantships (TAs)
- TAs assist faculty members with teaching duties, including grading, leading discussion sections, and tutoring students. In return, they receive a stipend and tuition remission.
- Example: At Stanford University, graduate students can apply for teaching assistantships, which include a stipend and tuition coverage, particularly in the humanities and social sciences.
- Fellowships
- Fellowships are prestigious awards that often provide full funding, including tuition, fees, and a living stipend. They are typically awarded based on academic excellence and research potential.
- Example: The University of Chicago offers the Harper Fellowship, a highly competitive fellowship that provides full tuition and a generous stipend to doctoral students across various disciplines.
- External Scholarships
- In addition to university-provided aid, there are numerous external scholarships available from organizations, foundations, and government agencies. These scholarships often have specific eligibility criteria and application processes.
- Example: The Fulbright Program offers scholarships to graduate students pursuing research or study in the United States. The program covers tuition, living expenses, and provides additional support for research activities.
- Employer Sponsorship
- Some graduate students may receive financial support from their employers, particularly if their studies are related to their job. Employer sponsorship can cover tuition and other expenses in exchange for a commitment to return to the company after graduation.
- Example: Many MBA programs, such as those at Harvard Business School and the Wharton School at the University of Pennsylvania, have students who are sponsored by their employers.
How to Secure Scholarships and Financial Aid
Securing scholarships and financial aid requires careful planning and proactive effort. Here are some steps to increase your chances of receiving financial support:
- Start Early
- Begin researching scholarships and financial aid opportunities as soon as possible. Many applications have early deadlines, and gathering the necessary materials (such as recommendation letters and essays) can take time.
- Research Thoroughly
- Investigate all available financial aid options at the universities you are applying to. Visit the financial aid offices, review the university websites, and reach out to current students or alumni for insights.
- Tailor Your Applications
- Customize your scholarship and financial aid applications to highlight your strengths and align them with the criteria of the awards. A well-tailored application can significantly increase your chances of success.
- Prepare a Strong Personal Statement
- Many scholarships require a personal statement or essay. This is your opportunity to demonstrate your passion for your field of study, your academic achievements, and your long-term goals. Make sure your statement is clear, compelling, and free of errors.
- Seek Faculty Recommendations
- Strong letters of recommendation from faculty members or professionals in your field can greatly enhance your application. Choose recommenders who know you well and can speak to your academic abilities and potential.
- Apply for Multiple Scholarships
- Don’t limit yourself to applying for just one or two scholarships. The more scholarships you apply for, the better your chances of securing funding.
- Consider External Funding Sources
- In addition to university-specific scholarships, look for external scholarships from government agencies, non-profits, and professional organizations. These can provide additional funding and may have less competition than university-based awards.
Notable Scholarships and Fellowships
Here are some notable scholarships and fellowships available to graduate students at top U.S. universities:
- Rhodes Scholarship: A prestigious international scholarship that allows students to study at the University of Oxford, covering all expenses.
- Marshall Scholarship: A scholarship for U.S. students to study in the UK, covering tuition, living expenses, and travel costs.
- National Science Foundation (NSF) Graduate Research Fellowship: Provides three years of financial support, including a stipend and tuition coverage, for students in STEM fields.
- Ford Foundation Fellowship: Supports graduate students in pursuing careers in academia, with a focus on promoting diversity in higher education.
- Gates Cambridge Scholarship: Covers full costs for graduate study at the University of Cambridge, available to outstanding students from outside the UK.
Conclusion
Graduate education at a top U.S. university is an investment that can lead to exceptional career opportunities. However, the cost can be a barrier for many students. By exploring and applying for scholarships, fellowships, and other financial aid options, students can significantly reduce the financial burden and focus on their academic and professional goals. With careful planning and persistence, securing funding for graduate studies is an achievable goal.

